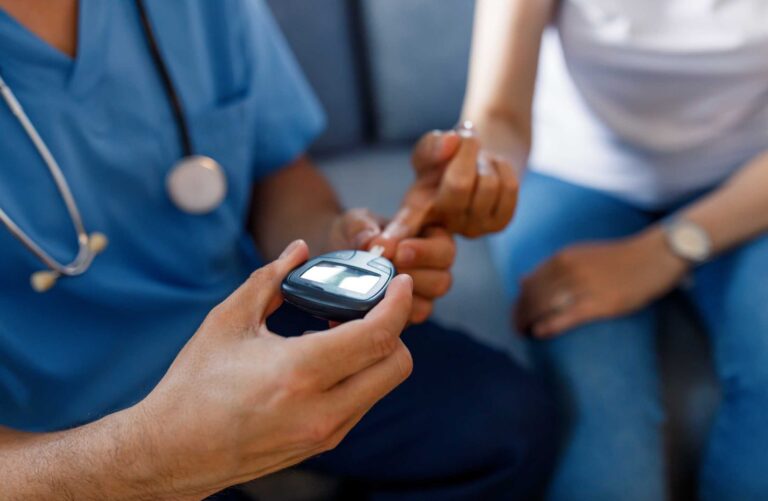
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how your body processes/metabolizes glucose (sugar), a vital source of energy. Effective management of this condition requires a holistic approach involving lifestyle changes, consistent monitoring, and sometimes, medication. Here are seven essential strategies to help you manage type 2 diabetes more efficiently:
Adopt a Balanced Diet
Eating a nutritious, well-balanced diet is one of the most crucial components for managing type 2 diabetes. The right foods can help stabilize your blood sugar levels and prevent dangerous spikes. A healthy and balanced diet consists of eating nutritious-dense foods in appropriate portions while avoiding or limiting non-nutritious foods. When looking to eat healthy, keep it simple. Aim to eat foods that provide the most nutrition per calorie. Many of these items provide your body with essential nutrients it needs to stay healthy.
These include:
- Whole Foods: Prioritize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. These foods are rich in nutrients and low in refined sugars, making them ideal for blood sugar management.
- Watch Carbohydrate Intake: Carbohydrates directly impact blood sugar levels. Opt for complex carbs like whole grains and legumes, and be mindful of portion sizes to avoid overeating.
For more tips on eating healthy with type 2 diabetes, check out this guide on successful habits of healthy eaters.
You can also try these lip-smacking-diabetes-friendly desserts.
Exercise Regularly
Physical activity is a cornerstone of effective diabetes management because it helps your body use insulin more efficiently. Regular exercise offers several benefits, including:
- Weight Loss: As you lose weight, being active helps you maintain it.
- Lower Blood Sugar: Exercise helps reduce blood sugar levels.
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Regular physical activity boosts your body’s sensitivity to insulin, helping to keep your blood sugar within a normal range.
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, such as walking, cycling, or swimming, each week. Incorporate strength training exercises like weightlifting to build muscle and improve insulin sensitivity. Stay active throughout the day by taking short walks, using stairs, and standing up regularly if you have a sedentary job.
You can use these top 10 wellness tracking apps for a healthier you in 2024
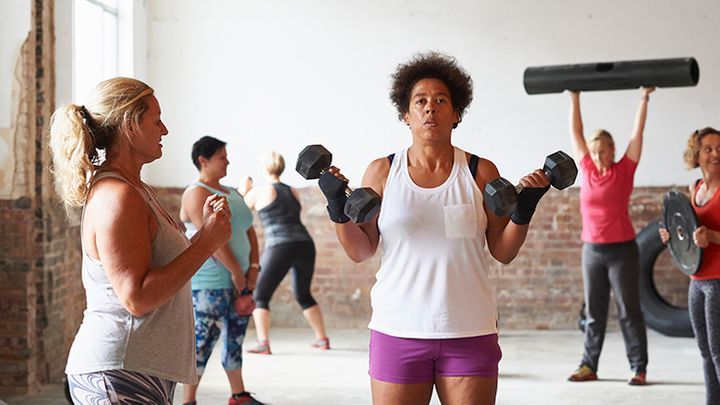
Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
Regularly checking your blood sugar levels is essential for understanding how your body responds to different foods, activities, and medications. Here’s how to stay on top of your levels:
- Keep a Log: Maintain a record of your blood sugar readings, noting the time of day, your meals, and activities. This can help you and your healthcare provider fine-tune your management plan.
- Follow Your Target Range: Work with your healthcare provider to determine your ideal blood sugar range and aim to keep your levels within this range as much as possible. This can help prevent complications associated with diabetes, such as nerve damage and heart disease.
Take Medications as Prescribed
Medications play a critical role in managing type 2 diabetes for many people. This may include oral medications, insulin, or other injectable medications. Common medications include:
- Metformin: Lowers glucose production in the liver and improves insulin sensitivity.
- Sulfonylureas: Stimulate the pancreas to release more insulin. Examples include glyburide (DiaBeta, Glynase), glipizide (Glucotrol XL) and glimepiride (Amaryl)
- Glinides: Stimulate rapid insulin release but have a shorter duration of action than sulfonylureas. But their effect in the body is shorter. Examples include repaglinide and nateglinide.
- Thiazolidinediones: make the body’s tissues more sensitive to insulin.
- DPP-4 Inhibitors: help reduce blood sugar levels but tend to have a very modest effect.
- GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: injectable medications that slow digestion and help lower blood sugar levels. Their use is often associated with weight loss, and some may reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke.
- SGLT2 Inhibitors: Help the kidneys remove glucose through urine, reducing blood sugar levels.
Ensure you take your medications exactly as prescribed. Missing doses or taking medications incorrectly can lead to uncontrolled blood sugar levels and increase the risk of complications. For more details on diabetes medications, visit Medications for type 2 diabetes.

Manage Stress
Stress can negatively impact blood sugar levels, making diabetes management more challenging. When you’re stressed, your body releases hormones that can increase blood sugar. Here’s how to manage stress effectively:
- Practice Stress-Reduction Techniques: Incorporate activities like deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga into your routine to keep stress levels in check.
- Get Enough Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night, as poor sleep can elevate blood sugar levels.
Read more on 10 Quick Tips About Power Naps That Will Transform Your Line
Reduce Alcohol Intake
Alcohol can complicate diabetes management by affecting blood sugar levels and contributing to weight gain. Follow these guidelines:
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Keep your intake to moderate levels—no more than one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men.
- Choose Wisely: Opt for drinks that are lower in sugar and calories, and avoid binge drinking.
For more on alcohol and diabetes, check out drinking alcohol with diabetes.
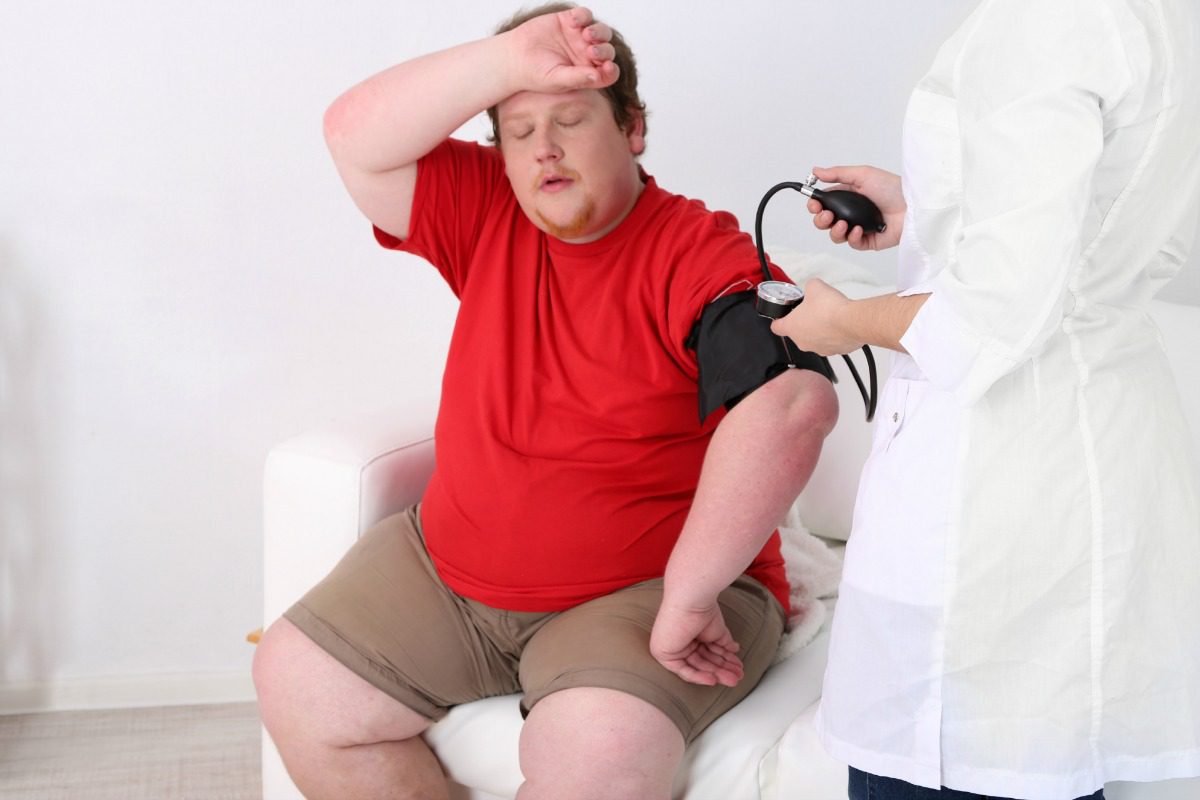

Maintain a Healthy Weight
Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is vital for managing type 2 diabetes. Even a modest weight loss can improve your body’s ability to regulate blood sugar. Here’s how:
- Set Realistic Goals: Work with your healthcare provider or a dietitian to set achievable weight-loss goals.
- Adopt Healthy Habits: Combine a balanced diet with regular physical activity to lose weight safely and maintain it long-term.
For more advice on weight management, check 10 healthy tips on how to lose weight naturally without exercise.
Conclusion
Managing type 2 diabetes efficiently requires a comprehensive approach that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, proper medication, and stress management. By following these seven strategies, you can take control of your blood sugar levels, reduce the risk of complications, and enjoy a healthier life. Always consult with your healthcare provider to tailor your diabetes management plan to your specific needs.